1. What is Java?
Java is a programming language and a platform introduced by Sun Micro-systems in 1995. Java is a high level, robust, secured and object-oriented programming language.
2. What is platform? Which platform Java is used?
Any hardware or software environment in which a program runs, is known as a platform. Since Java has its own runtime environment (JRE) and API, it is called platform. It is also called as WORA (Write Once Run Anywhere), supports different Operating System once program is stored in the .java extension.
3.Where it is used?
4. Java Platforms / Editions
2. What is platform? Which platform Java is used?
Any hardware or software environment in which a program runs, is known as a platform. Since Java has its own runtime environment (JRE) and API, it is called platform. It is also called as WORA (Write Once Run Anywhere), supports different Operating System once program is stored in the .java extension.
3.Where it is used?
- Desktop Applications such as acrobat reader, media player, antivirus etc.
- Web Applications such as irctc.co.in, javatpoint.com etc.
- Enterprise Applications such as banking applications.
- Mobile
- Embedded System
- Smart Card
- Robotics & Games etc
4. Java Platforms / Editions
- Java SE (Java Standard Edition)
- Java EE (Java Enterprise Edition) - It is built on the top of Java SE platform. It includes topics like Servlet, JSP, Web Services, EJB, JPA etc.
- Java ME (Java Micro Edition) - It is a micro platform which is mainly used to develop mobile applications.
- JavaFx It is used to develop rich internet applications. It uses light-weight user interface API.
5. Types of Java Applications
- Standalone Application
- Web Application
- Enterprise Application
- Mobile Application
6. Java Version History
There are many java versions that has been released. Current stable release of Java is Java SE 10. JDK Alpha and Beta (1995)
- JDK 1.0 (23rd Jan, 1996)
- JDK 1.1 (19th Feb, 1997)
- J2SE 1.2 (8th Dec, 1998)
- J2SE 1.3 (8th May, 2000)
- J2SE 1.4 (6th Feb, 2002)
- J2SE 5.0 (30th Sep, 2004)
- Java SE 6 (11th Dec, 2006)
- Java SE 7 (28th July, 2011)
- Java SE 8 (18th March, 2014)
- Java SE 9 (21st Sep, 2017)
- Java SE 10 (20th March, 2018)
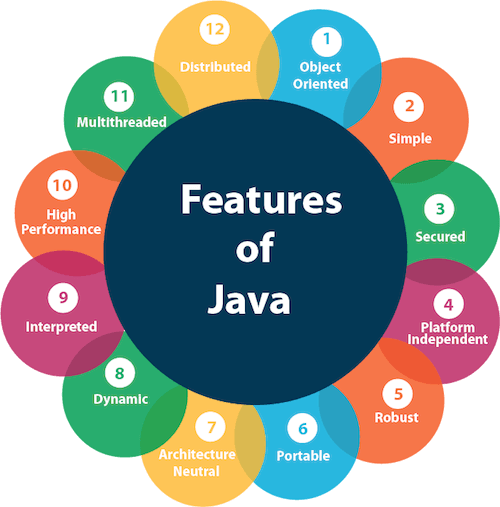
7. What are the features of JAVA?
1. Object-oriented: Java is Object-oriented programming language. Everything in Java is an object. -organize our software as a combination of different types of objects that incorporates both data and behavior -Object-oriented programming(OOPs) is a methodology that simplifies software development and maintenance by providing some rules
2. Simple: Java is very easy to learn and its syntax is simple, clean and easy to understand. Removed explicit pointers, operator overloading etc. Automatic Garbage Collection in java. Basic concepts of OOPs are: (i) Encapsulation (ii) Abstraction (iii) Inheritance and (iv)Polymorphism
3. Secured: Java is best known for its security. With Java, we can develop virus-free systems. Java is secured because:
(i) No explicit pointer
(ii) Java Programs run inside virtual machine sandbox
Classloader:
Classloader in Java is a part of the Java Runtime Environment(JRE)
which is used to dynamically load Java classes into the Java Virtual
Machine.
Bytecode Verifier:
It checks the code fragments for illegal code that can violate access right
to objects.
Security Manager:
It determines what resources a class can access such as reading and
writing to the local disk.
4. Platform Independent: Java is platform independent because it is different from other languages like C, C++ etc. There are two types of platforms software-based and hardware-based. Java provides software-based platform. The Java platform differs from most other platforms in the sense that it is a software-based platform that runs on the top of other hardware based platforms.
It has two components:
- Runtime Environment
- API(Application Programming Interface)
5. Robust:
 It uses strong memory management.
It uses strong memory management.
- There are lack of pointers that avoids security problem.
 There is automatic garbage collection in java.
There is automatic garbage collection in java. 
- There is exception handling and type checking mechanism in java.
6. Portable: Java is portable because it facilitates you to carry the java bytecode to any platform.
7. Architecture-neutral: Java is architecture neutral because there is no implementation dependent features e.g. size of primitive types is fixed.
In C programming, int data type occupies 2 bytes of memory for 32-bit architecture and 4 bytes of memory for 64-bit architecture. But in java, it occupies 4 bytes of memory for both 32- and 64-bit architectures.
8. High-performance: Java is faster than traditional interpretation since bytecode is "close" to native code still somewhat slower than a compiled language (e.g., C++). Java is an interpreted language.
9. Multi-threaded: A thread is like a separate program, executing concurrently.
10. Distributed: Java is distributed because it facilitates us to create distributed applications in java. RMI and EJB are used for creating distributed applications.
8. Difference between C++ and JAVA.
Comparison Index
|
C++
|
Java
|
Platform-independent
|
C++
is platform-dependent.
|
Java
is platform-independent.
|
Mainly
used for
|
C++
is mainly used for system programming.
|
Java
is mainly used for application programming. It is widely used in window,
web-based, enterprise and mobile applications.
|
Goto
|
C++
supports goto statement.
|
Java
doesn't support goto statement.
|
Multiple
inheritance
|
C++
supports multiple inheritance.
|
Java
doesn't support multiple inheritance through class. It can be achieved by
interfaces in java
|
Operator
Overloading
|
C++
supports operator overloading.
|
Java
doesn't support operator overloading.
|
Pointers
|
C++
supports pointers. You can write pointer program in C++.
|
Java
supports pointer internally. But you can't write the pointer program in java.
It means java has restricted pointer support in java.
|
Compiler
and Interpreter
|
C++
uses compiler only.
|
Java
uses compiler and interpreter both.
|
Call
by Value and Call by reference
|
C++
supports both call by value and call by reference.
|
Java
supports call by value only. There is no call by reference in java.
|
Structure
and Union
|
C++
supports structures and unions.
|
Java
doesn't support structures and unions.
|
Thread
Support
|
C++
doesn't have built-in support for threads. It relies on third-party libraries
for thread support.
|
Java
has built-in thread support.
|
Documentation
comment
|
C++
doesn't support documentation comment.
|
Java
supports documentation comment (/** ... */) to create documentation for java
source code.
|
Virtual
Keyword
|
C++
supports virtual keyword so that we can decide whether or not override a
function.
|
Java
has no virtual keyword. We can override all non-static methods by default. In
other words, non-static methods are virtual by default.
|
unsigned
right shift >>>
|
C++
doesn't support >>> operator.
|
Java
supports unsigned right shift >>> operator that fills zero at the
top for the negative numbers. For positive numbers, it works same like
>> operator.
|
Inheritance
Tree
|
C++
creates a new inheritance tree always.
|
Java
uses single inheritance tree always because all classes are the child of
Object class in java. Object class is the root of inheritance tree in java.
|


No comments:
Post a Comment